Understanding Septal Infarct: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
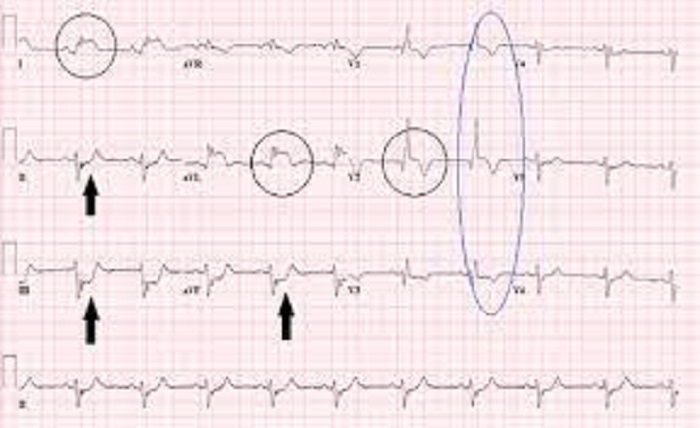
Septal infarct is a medical condition characterized by damage to the septum, which is the wall that separates the left and right sides of the heart. This condition is often associated with heart attacks and can have significant implications for a person’s cardiovascular health. In this blog post, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options for septal infarct, shedding light on this important medical condition.
What is Septal Infarct?
Septal infarct occurs when the blood supply to the septum is interrupted, leading to tissue damage. This interruption usually happens as a result of a blockage in one or more of the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart. The blockage is often caused by a blood clot or the buildup of fatty deposits known as plaque.
Causes of Septal Infarct:
- Coronary Artery Disease: Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the most common cause of septal infarct. It occurs when the coronary arteries, which are responsible for delivering oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle, become narrow or blocked. This can happen due to the accumulation of plaque, leading to reduced blood flow and increasing the risk of septal infarct.
- Heart Attack: Septal infarct can also be a consequence of a heart attack, medically referred to as a myocardial infarction. During a heart attack, a section of the heart muscle is deprived of oxygen due to a sudden blockage in the coronary artery. If the affected area includes the septum, it can result in septal infarct.
Symptoms of Septal Infarct:
- Chest Pain: Chest pain is a hallmark symptom of septal infarct. The pain may be severe and persistent, often radiating to the arms, jaw, or back. It is important to note that chest pain can have various causes, so it is essential to seek immediate medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Shortness of Breath: Septal infarct can cause difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity or even at rest. This occurs due to the compromised function of the heart’s pumping ability, resulting in reduced oxygen supply to the body.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): An electrocardiogram is a diagnostic tool used to assess the electrical activity of the heart. It can help identify abnormal patterns associated with septal infarct, such as specific changes in the heart’s electrical signals.
- Cardiac Imaging: Various imaging techniques, including echocardiography, cardiac MRI, and coronary angiography, may be utilized to visualize the heart’s structure and identify any damage to the septum.
- Medications: Treatment for septal infarct often involves medications aimed at relieving symptoms, reducing the workload on the heart, and preventing further complications. These may include antiplatelet agents, beta-blockers, and ACE inhibitors.
- Revascularization Procedures: In cases where the blockage in the coronary artery is severe, revascularization procedures may be necessary. These procedures, such as angioplasty or bypass surgery, aim to restore blood flow to the heart by removing or bypassing the blockage.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes:
Prevention plays a vital role in reducing the risk of septal infarct and other cardiovascular diseases. Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly contribute to maintaining heart health. This includes:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity on a regular basis can help improve cardiovascular fitness and reduce the risk of coronary artery disease.
- Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can promote heart health and help prevent the buildup of plaque in the arteries.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including septal infarct. Quitting smoking can have immediate and long-term benefits for heart health.
Conclusion:
Septal infarct is a condition that warrants attention due to its potential impact on cardiovascular health. Recognizing the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options is crucial for timely intervention and management. By adopting a healthy lifestyle and seeking medical advice, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce the risk of septal infarct and promote overall heart health. Remember, prevention is key, and early detection can save lives.




